Interactive Book: Final Report (GSoD 2020 - Daniel)
This is the final report for Google Season of Docs 2020 project CircuitVerse Interactive Book Consolidation and Improvements
Proposal abstract
CircuitVerse is an open source project aiming to provide a platform where circuits can be designed and simulated using a web-based graphical user interface. The logic simulator can be used to design up to complete CPU implementations, although it is designed primarily for educational use. Besides the technical documentation for the software, an online interactive book guides the user in learning digital logic design. The book allows the user to try out circuits directly from within the book for an interactive experience.
The book is in an early state of development and is currently lacking some relevant sections, the general structure is loose in terms of a flow connecting the different sections, and requires more detailed content. Moreover, according to the organisation, there are not guidelines to help contributors to collaborate to the project nor is a plan or road-map to guide contributions on which contents are needed and with which priority.
The aims of this proposal are to collaborate with the mentors to create contribution guidelines, produce a topic development plan and contribute with improving current content as well as create new content according to the development plan.
Copy of the original full proposal
Structure of the proposed documentation (excerpt from original proposal)
The interactive book has the potential to be useful for a broad audience ranging from amateur electronic hobbyist and secondary education students to tertiary education students and professionals in need of refreshing or strengthening their skills in digital logic circuits.
In order to address the heterogeneity in the book’s users a “multi-layer” structure is proposed, where each layer correspond to increasing level of complexity and theoretical depth of the contents.
Therefore, the documentation’s structure grows in two dimensions, the first dimension corresponds to the logical or traditional sequence of topics in digital logic systems, while the second dimension represents the level.
For simplicity, only three layers of complexity are defined for each topic, corresponding to basic, medium and advanced levels.
Proposed goals
All the proposed goals have been completed.
- Produce a first draft of contribution guidelines for the Interactive Book project.
- Outline a development plan for the book’s topics.
- Rewrite and restructure current content.
- Create new content according to the development plan.
Detailed activities agreed with mentors
The following activities were agreed with the mentors. All of the activities have been carried out.
- Analyse guidelines from other similar projects
- Write the “contribution guidelines” document
- Review/discuss proposed structure
- Rank sections into a prioritised list
- Re-structure current content according to proposed structure
- Create stubs for new sections
- Generate content according to the prioritised list
The content development plan
The content development plan had the following steps:
- Rearrange current content intro new tree structure
- Create content which is currently not covered
- Improve sections created from current content (as much as possible, given the duration of the project)
State of the project
Currently, the CircuitVerse Interactive Book new version is in beta stage. It is temporarily available in the following GitHub repositories:
It includes the new structure as well as the re-organised previous content and new content. The new content embeds new interactive circuits designed with the CircuitVerse simulator.
The previous content’s style and the new content’s one are not yet consistent. Also, some interactive code in JavaScript is not working properly in the new version. Issues have been created to work on these.
The previous content still needs more clean-up, addition of proper references and links to the newer content when appropriate.
The first version of the contribution guidelines has been released. It has been based on similar documents from other open source projects, such as Wikibooks, the Linux Documentation Project and OpenStreetMap. It is expected that this document will evolve together with the community development around the book project. Also, a license and licensing procedure was proposed and is part of the contribution guidelines, since the previous contributions were not under any licensing scheme.
Pull requests
The following pull request are associated to the contributions to the documentation repository in GitHub:
- First PR for GSoD 2020 Interactive Book project
- GSoD2020 new Interactive Book structure
- GSoD2020 Current book contents relocated into the new structure
- GSoD2020 New sections, basic level contents
Current book structure
The following list represents the new book’s structure (sections corresponding to the medium level are in bold, while advanced level sections are in bold and italics):
- Homepage
- Binary representation
- Binary numbers
- Negative quantities
- Number bases
- Encoding information
- Discrete quantities
- Binary algebra
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Division
- Boolean algebra
- Boolean functions
- Shannon decomposition
- IEEE Std 754
- Combinational SSI
- Symbols
- Logic gates
- Truth tables
- Logic families
- Universal gates
- Time behaviour
- Logic Design
- Functional description
- Implementation
- Canonical functions
- K-Maps
- Map-entered variables
- Quine McCluskey
- Binary cubes
- Combinational MSI
- MUX/DEMUX
- Encoders/Decoders
- Adders
- MUX-based functions
- Combinational LSI
- ROM
- ALU
- PLDs
- Sequential SSI
- Clock signals
- Flip-flops
- Latches
- Time diagrams
- Asynchronous systems
- Synchronous systems
- Sequential Design
- FSM
- Sequential synthesis
- Race conditions
- Flowchart diagrams
- MDS Diagrams
- Sequential MSI
- Registers
- Counters
- MSI based design
- Multipliers/Dividers
- Sequential LSI
- ROM-based µcontrollers
- FPGA
- Microprocessors
- Guidelines
Screenshots
This section include some screenshots from new book sections showcasing the available features and some of the style guidelines.
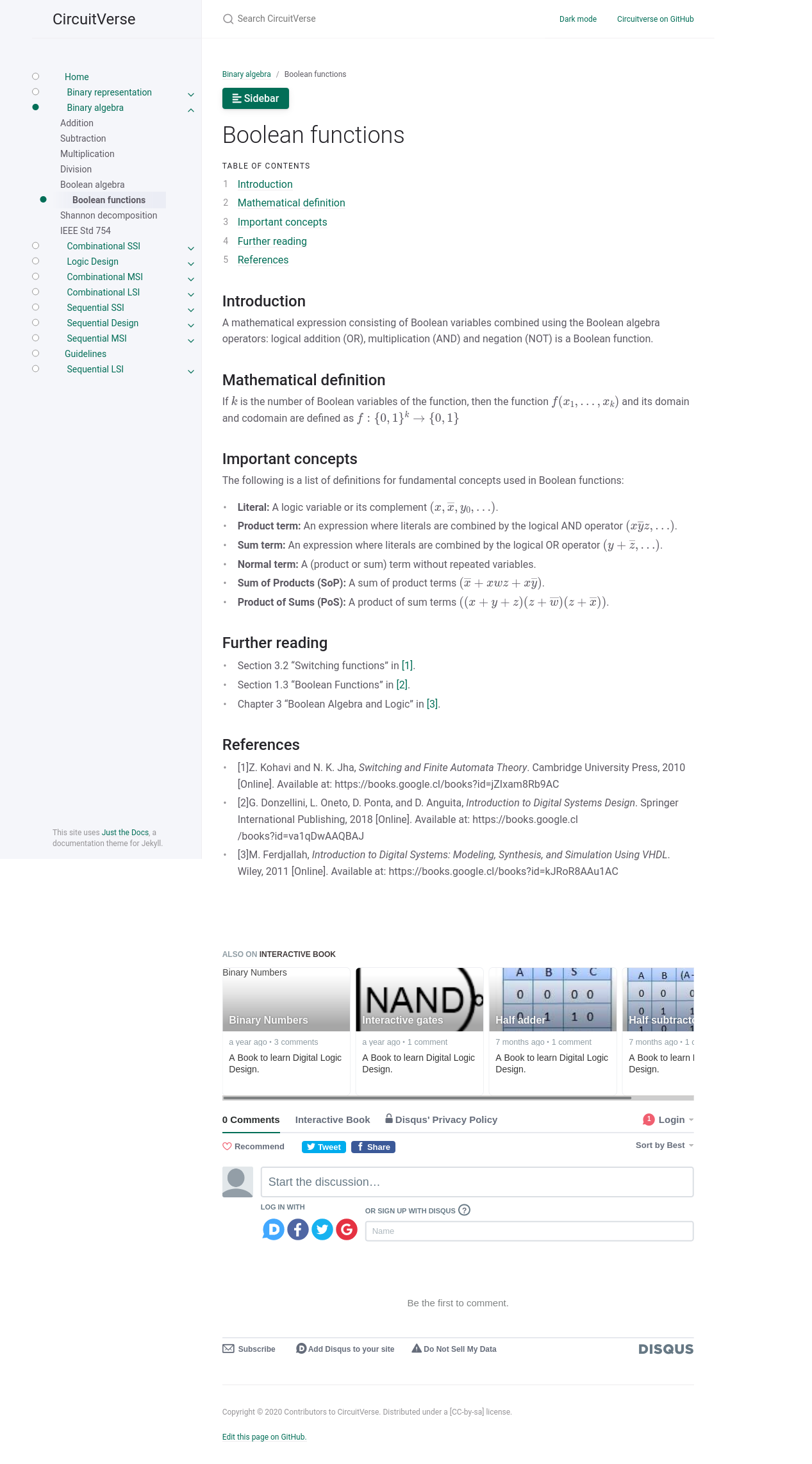
Boolean functions
The Boolean functions section screenshot shows the jekyll-spaceship and
jekyll-scholar plugins providing support for equations and bibliographies,
respectively.
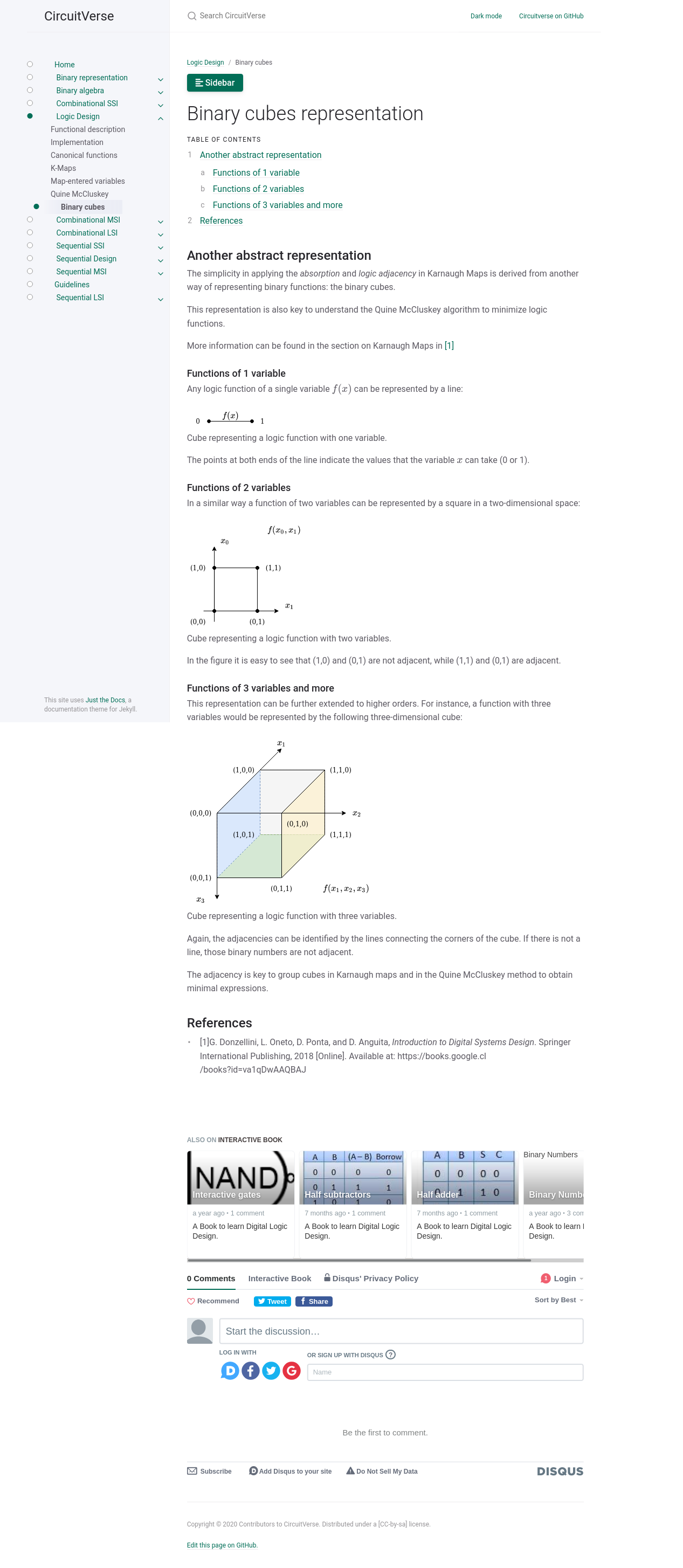
Binary cubes
The following screenshot from the Binary cubes representation section
show figures rendered using a dedicated template which provides captioned
figures (not available with pure markdown).
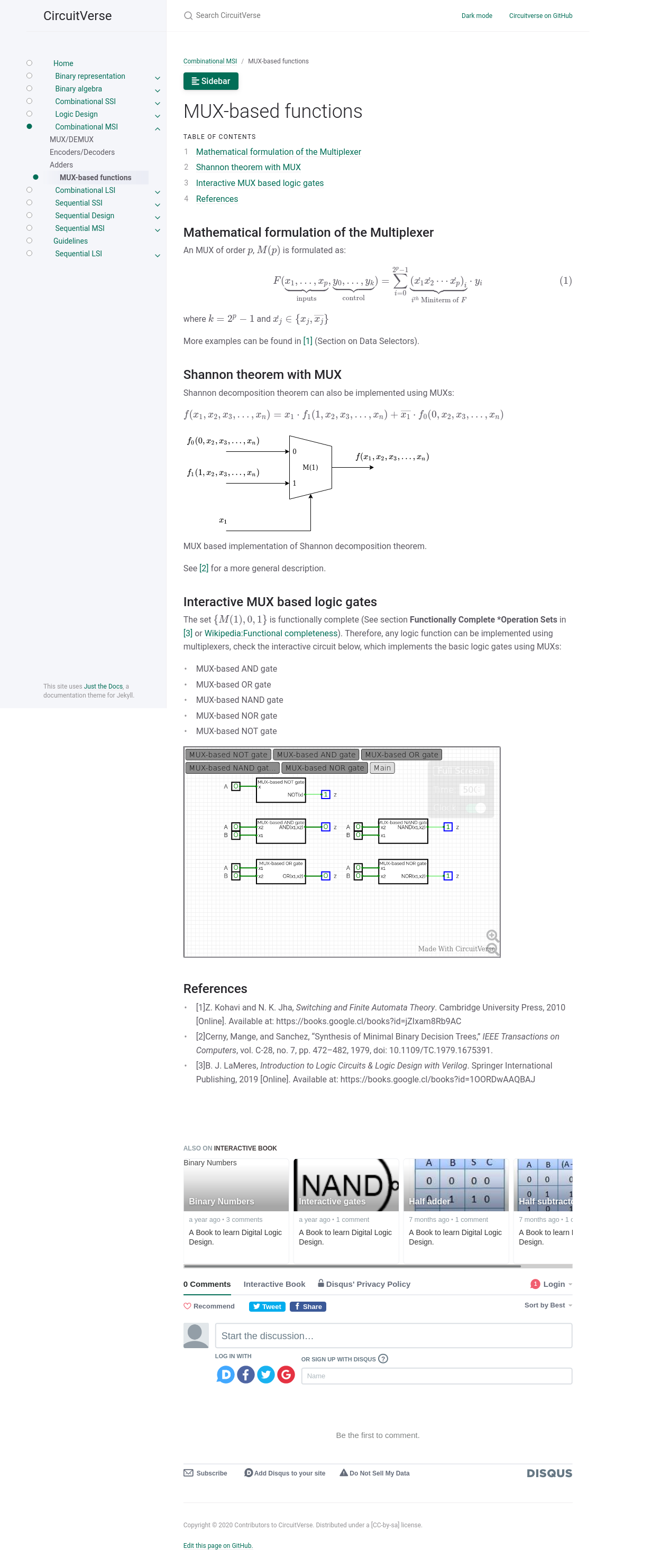
MUX-based functions
Besides the above mentioned features, one of the new interactive circuits can be seen in the next screenshot taken from MUX-based functions section.
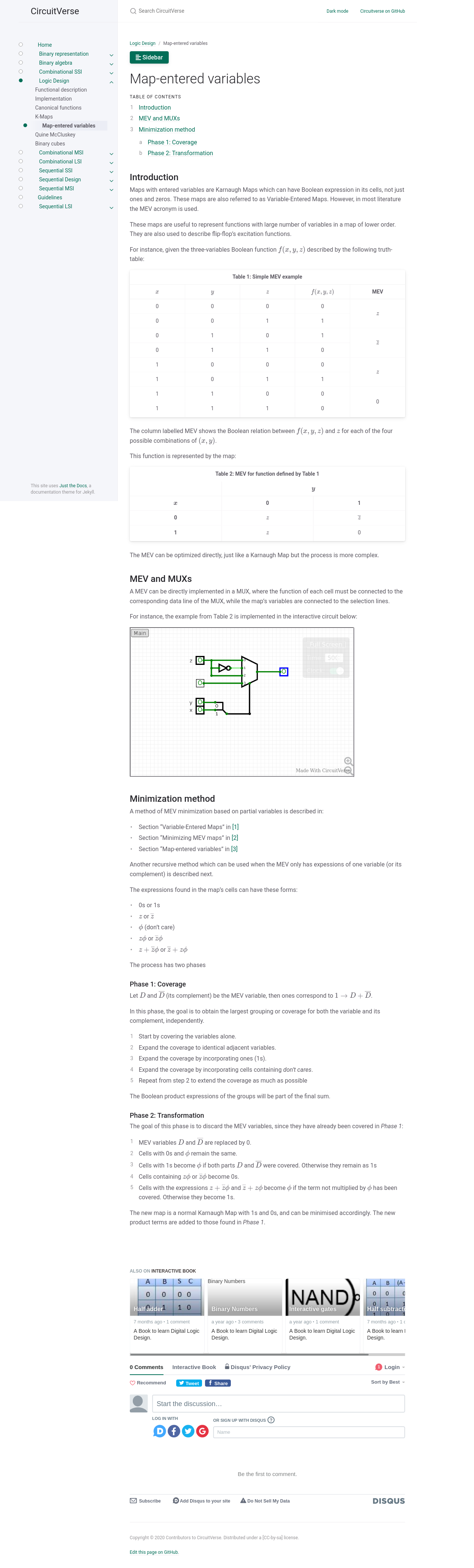
Map-entered variables
Another new feature provided by the jekyll-spaceship plugin is the possibility
to create more complex tables, including equations, multi-row and multi-column
cell spans, CSS override and more.
The tables in the section Map-entered variables depicted in the next screenshot
make use of some of these capabilities.
Also, these tables use the workaround for captioning described in the guidelines.
Challenges
Originally, it was expected that most of the project would be reviewing and re-arranging the previous content and creating the new sections. However, it was found at the beginning that the current Static Site Generator (SSG) used to deploy the book needed updating and improvements. Therefore, the newer upstream SSG version was installed from scratch, the book structure was implemented and the previous content was migrated. Nevertheless, the old SSG version had many custom made patches which were incompatible with the new version, so some updates in style and functionality have been created as issues and should be fixed soon in order to release the new version of the book.
Another challenge was that although the current SSG setup might be very well suited for general purpose documentation, book-like documentation is not well supported. To compensate the lack of features some plugins were added. To this end, it is recommended to evaluate in the near future whether the current infrastructure is the correct tool for maintaining a book-like documentation or it is better to migrate to another system with better support for the required tasks.
Learnings
Although I have been an advocate of Free and Open Source projects for more than two decades and have submitted a few single, “one-shot” contributions to a handful of projects, this is the first time for me to deeply interact with a thriving community in a young project with high potential. It has been a wonderful experience.
Yet, it is tempting to detour from the main goals set for the project, since there are so many interesting issues with which to collaborate. It is important to remain focused and follow the projected plan in order to reach the desired outcome in the given time.
Additional contributions
Besides the proposed goals and activities regarding the reorganisation and creation of the book’s contents, the following contributions were also made:
- Migration to a newer version of the SSG and theme for the book, this included
- Partial update and migration of the styles.
- Installation of additional plugins for added functionality.
- To simplify the creation of the many files in the new structure a simple script to generate them from templates in YAML format was created.
- The use of a CC-by-sa License was proposed when it was found that the previous content was lacking licensing information.
Future work
The following is a proposed list of possible future improvements:
- Create interactive content in the following topics:
- Example of animated minimisation using MEV method.
- Interactive demo for the Quine McCluskey method.
- Interactive example for ADC/DAC.
- Interactive example for floating point (and fixed point) representation of real numbers.
- Interactive kMap editor (source code available on GitHub).
- Conversion between number bases.
- CPU simulation/interactions (optionally, connected to a CPU implemented in CircuitVerse’s simulator, by transferring the ROM contents).
- Evaluate migration to a new infrastructure for the book.
- Fix JavaScript code for current interactions which is not working.
- Fix missing styles, add styles for new elements:
- equations
- captions (tables and figures)
- bibliographic references
- Add some features to the CircuitVerse simulator to provide examples to
specific topics:
- FPGA, PLDs: matrix interconnection (fuses).
- Since the book makes extensive use of figures, it might be possible to integrate a tool such as diagrams.net with CircuitVerse accounts. Then, just like the embedded circuit, the figures’ sources can be stored in the CircuitVerse’s server and the link embedded directly into the book (instead of copying image files into the assets directory).
- Include more interactive circuit examples:
- Circuits BCD, gray or other encoders/decoder for the section Encoding information.
- Examples in the MSI-based design section.
- Include a standard tool for diagrams such as draw.io/diagrams.net
- Make the styling consistent between previous and new content.
- Continue revising and improving previous content.
- Continuous improvement/maintenance of the book’s content.